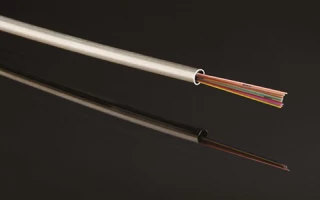
Fiber optic cable
Search
Coaxial cable (English abbreviation coax) is a type of cable used in radio frequency. The cross-sectional area of this cable consists of four interconnected items. The innermost is the live line, that is, the line that carries the signal. This tip is surrounded by an insulator with a high dielectric constant. There is a braid (or thin foil) of conductors around the insulator. This weave is grounded. There is a protective cover on the outermost part. It is very important that the braid of the cable consisting of conductors is grounded. Because in this way, the cable can pass near devices that create electromagnetic fields without being affected. On the other hand, this structure allows coaxial cables to be more elastic than other cables of their own thickness. The current carried by the coaxial cable is a very high frequency current such as VHF or UHF. The direction of the current changes millions of times per second. (VHF is the frequency range from 30 million to 300 million Hz, and UHF is the frequency range from 300 million to 3 billion Hz.)




![OPGW - 36B4-155 [91 -206,1]](https://optocom.az/storage/product/mg/656efc3a95d0d-656efc3a95d0f.webp)